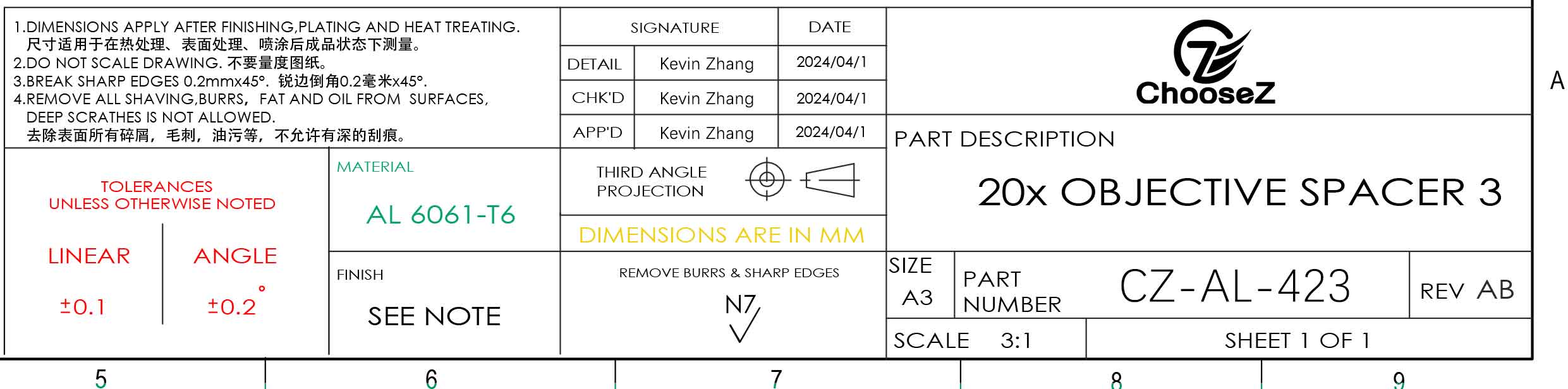
CNC Milling Machine Operation: Ready to Master the Key Skills?
POSTED ON May 09

This article provides a comprehensive analysis of the entire procedure, from examining the original designs to the last stages of machining. It goes over important procedures, factors, and methods for turning design ideas into final machined goods.
Study Drawing
When studying the drawing for CNC milling operations, several critical aspects need careful consideration:
Material Specifications
Determine if the material has specific requirements such as surface treatment compatibility. For instance, stainless steel typically requires passivation to prevent corrosion.
Dimensional Requirements
Evaluate both general dimensions and precision measurements specified in the drawing. Consider aspects like parallelism and positional tolerances to assess if your machining setup can meet the required tolerances for this order.
Compatibility Check
Verify if the material properties align with the capabilities of your CNC milling machine. Assess the machine's capacity to handle the required precision and complexity outlined in the drawing.
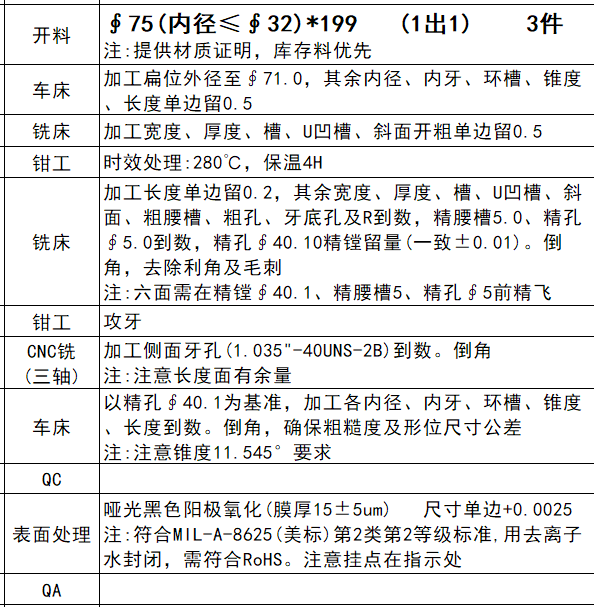
Scheduling the Process of Machining
Planning the machining process for CNC operations involves taking a number of important factors into account:
Selecting Appropriate Equipment (Milling or Turning)
Consider the geometry and needs of the part while deciding between a lathe and a milling machine. For cylindrical pieces, lathes are the best tool; for complex forms and profiles, milling machines are the best.
One or more operations
Find out if the part needs to be done in several steps or can be finished in one. For full machining of complex items, several setups and operations are frequently needed.
Outlining the Machining Goals for Every Stage
Determine the precise machining goals and intended results for every operation. This entails fulfilling the design specifications' geometric tolerances, surface finish requirements, and dimensional precision.
Choosing the Correct Device
When selecting the right equipment, keep the following in mind:
Know the machine's maximum precision capabilities based on its technical characteristics.
Determine if a single machine can do all tasks or if multiple machines are needed, particularly for complex pieces where separate setups may be needed for roughing and finishing.
Optimize machine utilization while striking a balance between efficient use and processing urgent orders, taking into account production line capacity and machine availability.
Material Selection
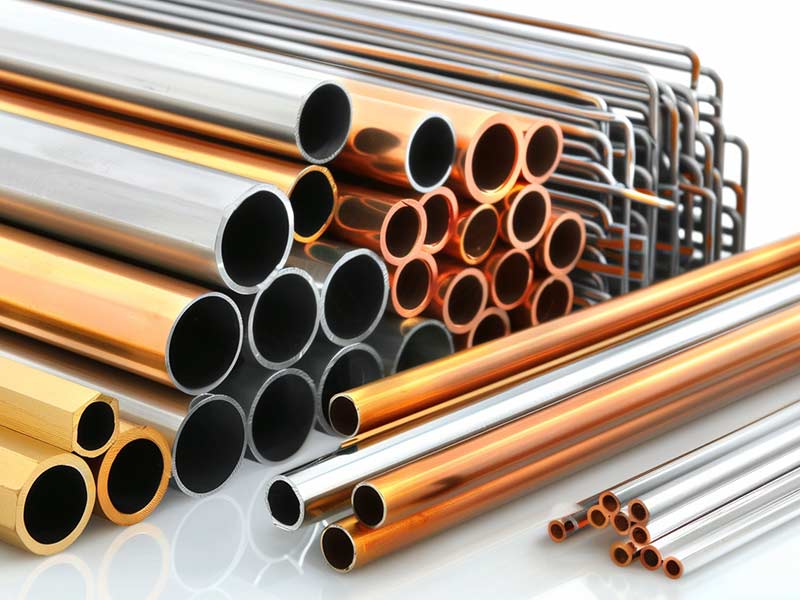
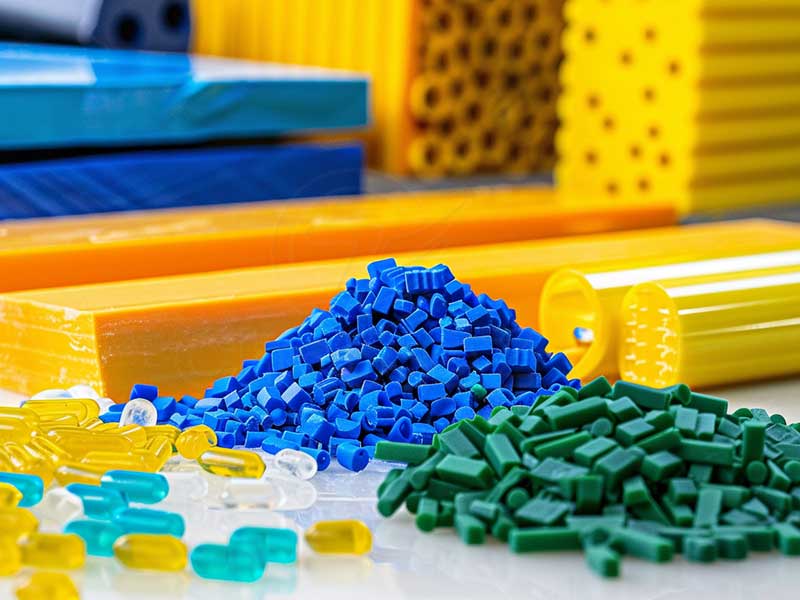


1、Material Selection according to Specifications:
Select the material parameters based on the requirements specified in the drawing.
To guarantee that machining operations are successful, get material reports from vendors.
2、Considering Processing Needs:
Depending on the intricacy of the machining and the needs of production, choose between starting with raw materials or pre-machined blanks..
3、Three Typical Material Types:
Steel Alloys: Including stainless steel, carbon steel, and tool steel.
Aluminum Alloys: Such as 6061-T6, 7075-T6, and aluminum extrusions.
Engineering Plastics: Like ABS, Nylon, and PEEK.
Exotic Metals: Titanium, Inconel, and other high-performance alloys used in specialized applications.
Tools and Fixtures
Toolpath Planning using CAD
To plan toolpaths for effective machining operations, use CAD software.
Take into account variables including tool engagement, tool changes, and cutting direction.
Tool Selection

Select the right tools according to the component geometry, machining complexity, and material characteristics.
Drills are often used for creating holes, ball-end mills are used for contouring, and end mills are used for general milling.
Fixture Design and Selection
Determine the fixtures needed depending on the size, shape, and machining processes of the part.
For complex items, special fixtures could be required to guarantee accuracy and stability during machining operations.
Optimizing Tool and Fixture Integration
Organize tool and fixture designs in a coordinated manner to save setup times and increase productivity.
For smooth operations, take into account elements like tool accessibility, clamping mechanisms, and tool changing procedures.
CNC Milling Machining Process
Blueprint Generation
Start by utilizing CAD software to create a thorough blueprint or technical drawing of the part.
As required by design standards, provide dimensions, tolerances, material specifications, and surface finish requirements.
CAD Model Development
Choosing CAD Software
CAD software alternatives that are popular are Autodesk Inventor, SolidWorks, Catia, and Creo.
Select software according to the experience level of your team, particular design requirements, and software compatibility with CNC machining software.
CAD Procedure Creation
1、Sketch and Digitize:
Use CAD software to digitize your initial rough sketches or 2D drawings.
2、Build 3D Models:
To create detailed, dimensioned 3D models from 2D drawings, use CAD software.
3、Detailing and Assembly:
Create fine details such as threads, fillets, and holes, then assemble parts as necessary.
4、Review and Validate:
Make sure the CAD model is fully reviewed and validated for design flaws and manufacturing viability.
5、Export and Document:
Create detailed drawings with requirements for CNC machining operations and export the finished CAD model in formats that are compatible.
CAM to CAD Conversion
The process of translating a finished CAD design into CNC programming—machine-readable instructions—comes next. Here's the procedure:
1、Comprehending CNC Terminology:
Convert CAD design instructions into a language that CNC machines can understand, usually G-code. During machining operations, G-code regulates variables such as feed rate and spindle speed.
2、CAM Software Integration:
To define CAM parameters like tooling, machine type, cutting speeds, and feed rates, integrate CAM software with CAD. The generation of G-code for CNC programs is streamlined by this integration.
3、Generating CNC Programs:
Create G-code programs by using toolpath strategies and CAM parameters. Because CNC programs are modifiable, machinists can adjust machining procedures as necessary.
4、CNC Program Optimization:
To guarantee accurate and effective machining, pay close attention to crucial elements including toolpath optimization, tool changes, and speed adjustments, particularly at corners or complex geometries.
5、Simulation and Verification:
To confirm tool movements, identify possible collisions, and make sure machining operations adhere to design parameters, simulate CNC programs.
6、Transferring Programs to CNC Machines:
Give the CNC milling machine or machining center the finished G-code or CNC software. The process from CAD design to CAM parameters and ultimately to CNC machining operations is finished with this stage.
Setting up CNC Milling Machine
To guarantee precise and effective machining operations, there are a few essential processes involved in setting up a CNC milling machine. The main components of a CNC milling machine configuration are as follows:
Machine Inspection
Check coolant fluid levels, flow rates, and types suitable for specific milling operations requiring heat dissipation. Proper coolant flow speed and type are crucial.
Verify machine maintenance details, ensuring that all machine components are in good working condition.
Ensure cleanliness of the workspace and machine environment for safe and efficient operations.
Check the air compressor supply if necessary for pneumatic systems.
Tool Installation
Follow CNC milling program instructions to load the cutting tools required for the machining process.
Set tool length offsets (TLO) accurately to ensure precise tool engagement during machining.
Workpiece Coordinate Setup
Establish the XY reference point for the workpiece based on CNC program instructions and machining requirements.
Determine the Z offset for workpiece fixtures to ensure proper tool engagement and machining accuracy.
Setting Parameters for CNC Milling

Feed rate (speed): During milling, the feed rate controls how quickly the cutting tool passes through the material. Surface finish and substance removal rate are impacted.
Spindle speed: The cutting tool's speed can be changed by regulating the spindle speed. Selecting the ideal spindle speed is essential for surface finish quality, cutting efficiency, and tool life.
Depth of Cut: The depth at which the cutting tool engages the workpiece with each pass is indicated by this measurement. Chip load, tool wear, and overall machining precision are all impacted.
The CNC milling machine is prepared to start milling operations in accordance with the programmed instructions when the setup is finished, including loading the CNC milling program, checking tools and calibrating offsets, setting up the workpiece, and making sure all safety checks are met.
Six Kep Points For CNC Milling Machining
1、Safety precautions: When using the machine, make sure that the proper safety protocols are followed, such as donning protective gear.
2、Program loading: Verify that the G code or CNC program is properly inserted into the machine control unit.
3、Tool Setup: In accordance with the application's specifications, cutting tools are installed and adjusted as needed.
4、Workpiece fixation: To firmly fix the workpiece on the machine tool table, use the proper clamps or accessories.
5、Parameter Configuration: Depending on the material and processing requirements, modify parameters like feed speed, spindle speed, and cutting depth.
6、Monitoring and Optimization: Monitor machining operations closely, adjust parameters as needed, and optimize processes for improved efficiency and quality.
Q&A For CNC Milling Machine Operation
Q:What safety precautions should be followed when operating a CNC milling machine?
A:Operators should wear appropriate safety equipment such as goggles and gloves, ensure the work area is clear of obstructions, and follow lockout/tagout procedures when necessary.
Q:How to load a program onto a CNC milling machine?
A:Programs are typically loaded into a CNC mill directly from the computer via a USB drive, network connection, or using compatible software.
Q:Which cutting tool types are frequently utilized in CNC milling?
A:The end mill, ball mill, face mill, and drill are examples of common cutting tools. Each is made for a particular kind of cutting material and activity.
Q:What factors determine the feed rate and spindle speed during milling?
A:Factors such as material type, tool diameter, depth of cut and desired surface finish affect feed rate and spindle speed settings.
Q:How can I make sure that the dimensions and placement in CNC milling are accurate?
A:Accuracy may be maintained through regular workpiece dimension checks utilizing precision measuring equipment, machine alignment, and proper tool calibration.
Q:What maintenance tasks are essential for CNC milling machines?
A:Three essential maintenance activities are to regularly lubricate moving parts, inspect tool holders and spindles, and calibrate machine axes.

Kevin Zhang
NPI Supervisor
Zhang has been working as an NPI (New Product Introduction) manager for more than ten years. Every endeavor gains energy from his vibrant personality. In his own time, Kevin plays soccer competitively and coaches neighborhood young teams, showcasing his leadership abilities both on and off the field.
You Might also Like
View all →

CNC Milling Machine Operation: Ready to Master the Key Skills?
Read More →

How Much Does CNC Machining Cost?
Read More →





