Decoding CNC Machining:
Definition,Processes, Components, and More

Basis About CNC Machining
CNC Machining Definition
CNC machining, short for Computer Numerical Control machining, refers to the automated manufacturing process controlled by computers to shape various CNC materials such as metal, plastic, or wood into custom-designed components. The precision and automation offered by CNC machines make them crucial in modern CNC manufacturing.
Brief History And Evolution
The roots of CNC machining history trace back to the 1940s when John Parsons and his team developed the concept of numerical control to enhance manufacturing efficiency for producing helicopter blades. Over the years, advancements in computer technology, automation, and tooling have revolutionized CNC machining, leading to its widespread adoption in various industries.
Importance In Modern Manufacturing
In contemporary manufacturing, precision CNC machining stands as a cornerstone due to its precision, repeatability, and efficiency. Its ability to produce intricate parts with high accuracy has significantly impacted industries such as aerospace, automotive, healthcare, and consumer electronics, enabling the creation of complex components that are integral to modern products.
Explanation,Components, Processes Of CNC Machining
Explanation of CNC (Computer Numerical Control)
What is CNC machining?CNC (Computer Numerical Control) refers to the automated control of machining tools and 3D printers through computer commands. It uses computer programs to execute precise movements of the tools, facilitating accurate and complex shapes in materials like metals, plastics, and composites.
Core Components and Elements of CNC Machines
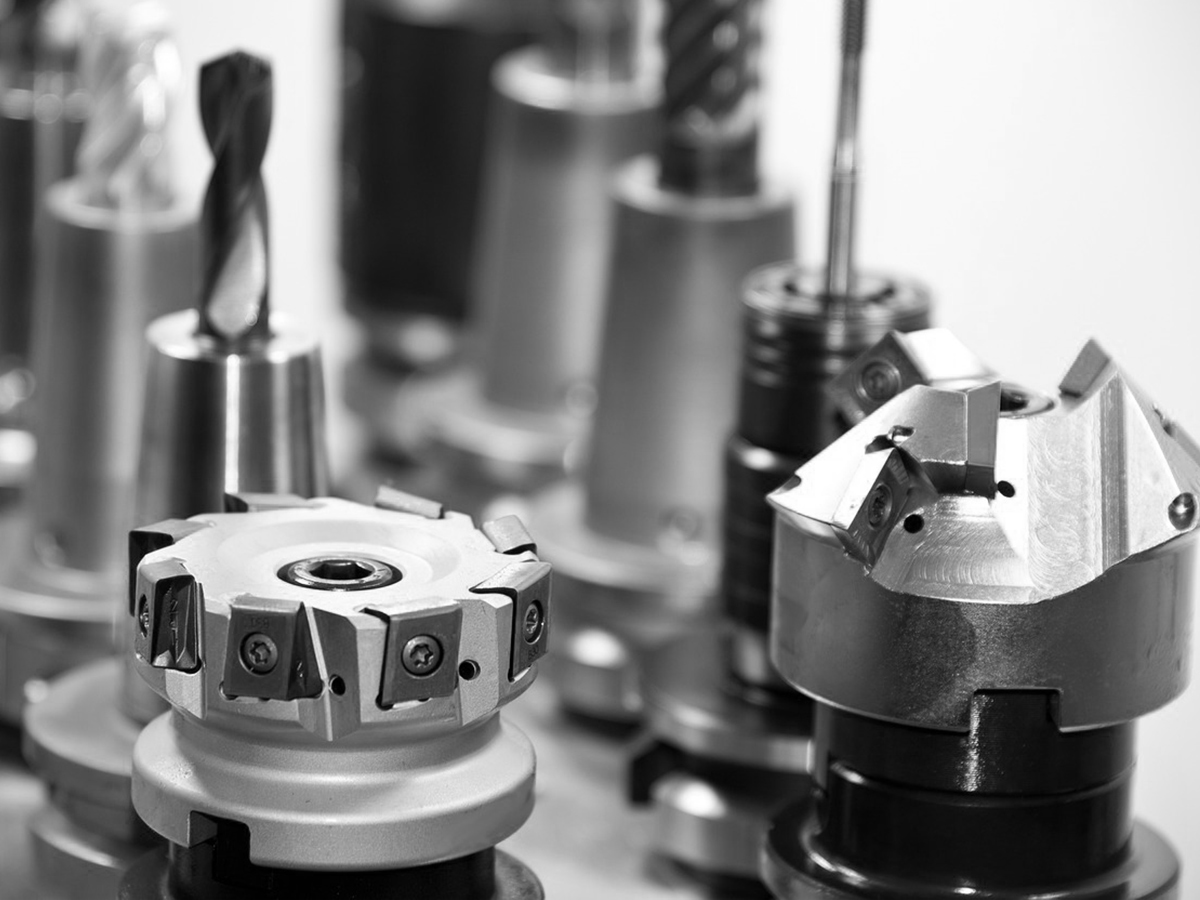

Processes of CNC Machining
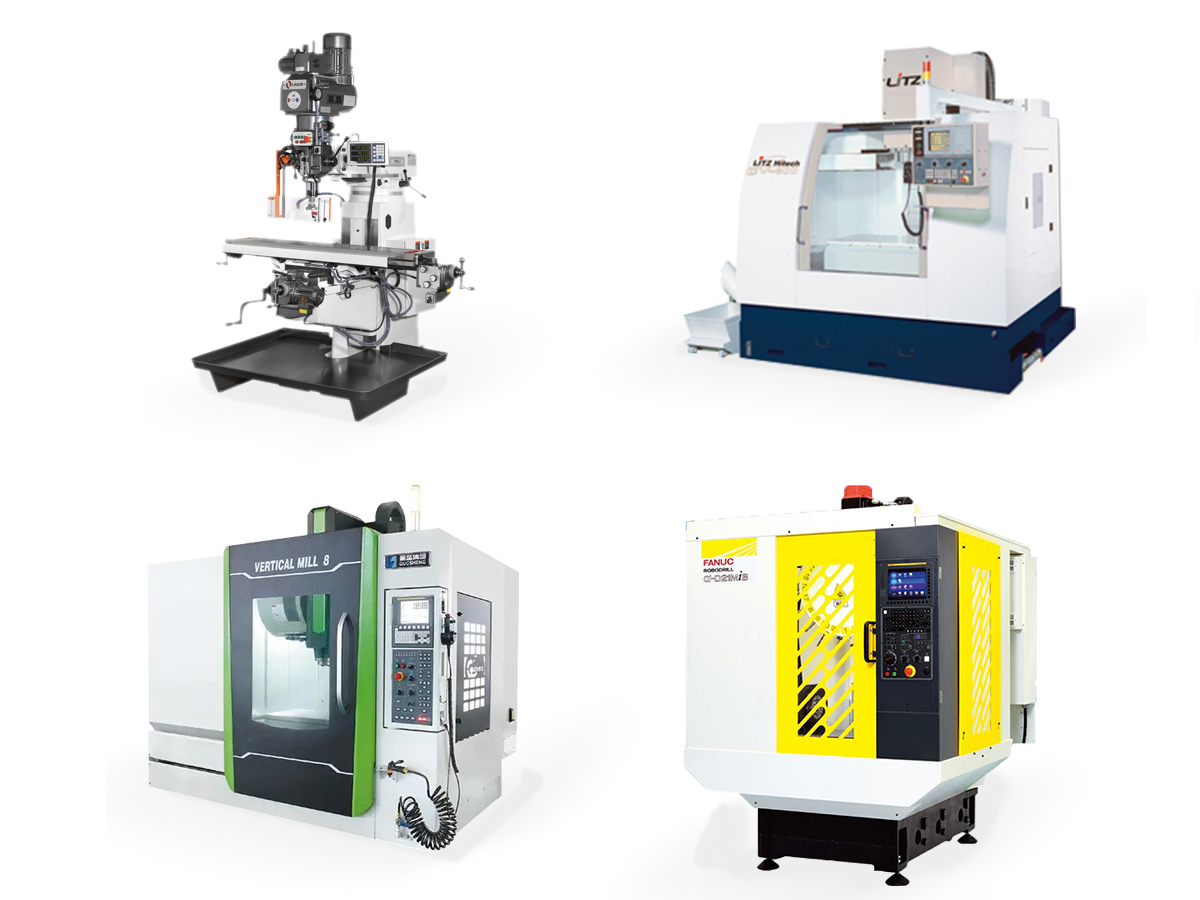
Different Types of CNC Machines
1 Milling Machines: Used for cutting and shaping solid materials using rotating cutters.
2 Lathes: Rotate the material on its axis to perform operations like cutting, drilling, and sanding.
3 Routers: Ideal for cutting and shaping wood, plastic, and metal using various bits.
4 Drilling Machines: Specialized in creating holes in workpieces.
Types | Functions and Applications | Advantages | Disadvantages |
Creating complex shapes, slots, and holes | Precision manufacturing | Initial high investment cost | |
Lathes | Cylindrical cuts, threading, and turning | ||
Routers | Intricate designs, engraving, and detailed cuts | ||
Drilling Machines | Creating holes accurately |
Specific Functions and Applications
1 Milling Machines: Suitable for creating complex shapes, slots, and holes.
2 Lathes: Efficient for cylindrical cuts, threading, and turning.
3 Routers: Ideal for intricate designs, engraving, and detailed cuts.
4 Drilling Machines: Perfect for creating holes accurately in different materials.
CNC Machining Advantages And Disadvantages
Advantages:
Precision and accuracy in manufacturing intricate parts. High production efficiency and repeatability. Reduced human error and increased safety.
Disadvantages:
Initial investment cost for CNC machining equipment and CNC machining software. Skilled personnel required for programming and CNC operation process. CNC machine maintenance and operational costs might be high.

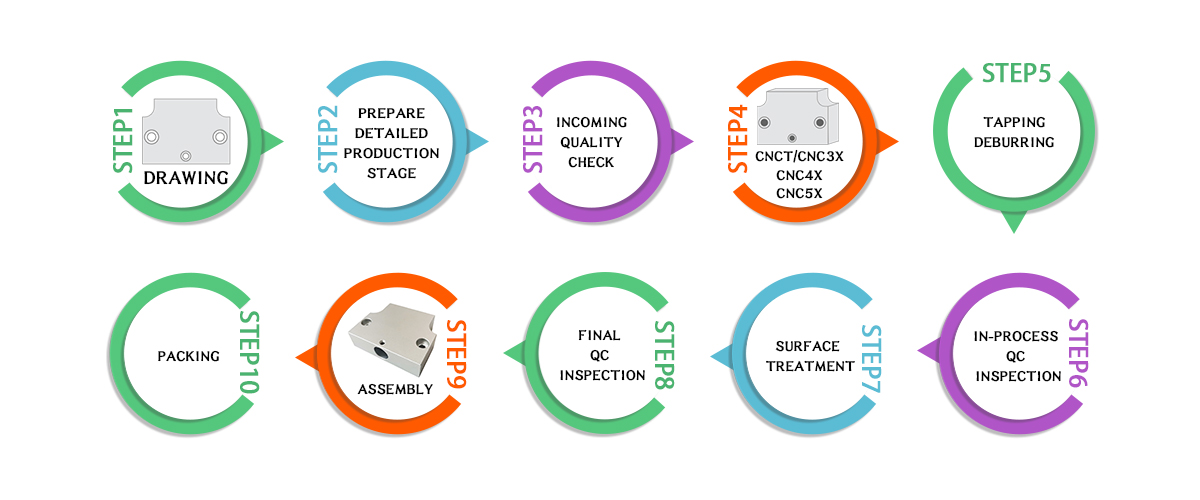
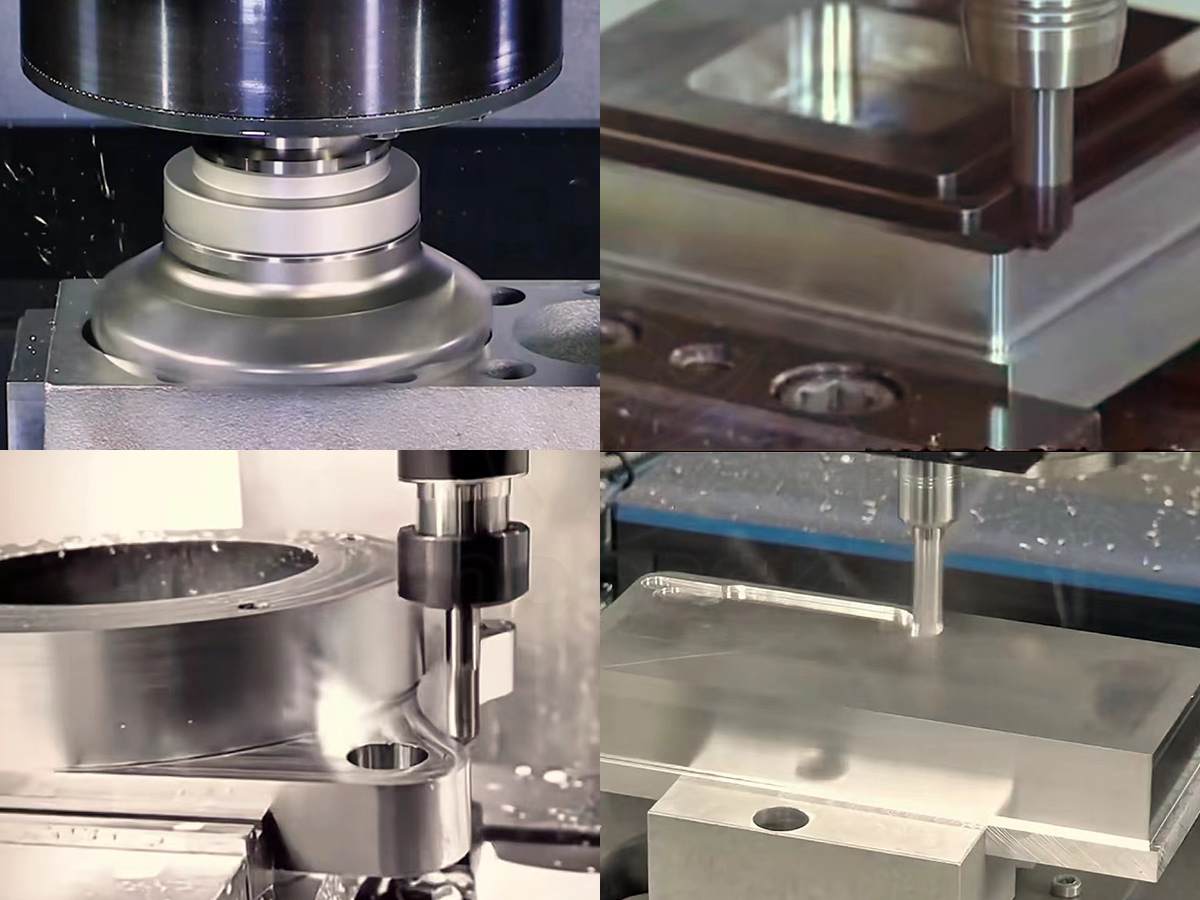
How CNC Machining Works
Detailed Explanation of the CNC Machining Process
CNC machining involves the utilization of pre-programmed computer software to control the movement of machinery and tools. These instructions precisely guide the cutting tools to sculpt raw materials into the desired shapes and dimensions. The process typically comprises several stages, including:
Design Creation: Engineers use CNC CAD software to craft intricate digital models of components or products. These models contain precise specifications for dimensions, angles, and features.
CAM Programming: CNC CAM software translates CAD models into machine instructions, generating toolpaths and optimizing cutting strategies for precision in CNC machining. This seamless integration enables precise digital designs to become tangible products.
Machine Setup: Raw material is loaded onto the CNC machines, and tools are prepared and installed according to the CAM-generated instructions.
Execution: The CNC machine precisely executes the programmed instructions, shaping the raw material into the desired form as per the design.
Quality Assurance: Throughout the process, frequent quality checks ensure the CNC machining parts adheres to specified tolerances and standards.
Applications of CNC Machining
Industries and Sectors Utilizing CNC Machining
Automotive Industry: CNC machining is extensively used in the automotive sector for manufacturing engine components, transmission parts, chassis, and intricate interior components.
Aerospace and Aviation: In aerospace, CNC machining is pivotal for producing complex and lightweight components such as turbine blades, aircraft structures, and critical engine parts.
Medical and Healthcare: CNC machining is integral to medical device manufacturing, producing surgical instruments, prosthetics, orthopedic implants, and specialized equipment with high precision.
Electronics and Technology: The electronics industry relies on CNC machining for manufacturing circuit boards, housings for electronic devices, and intricate components for smartphones, computers, and more.
Industrial Manufacturing: Numerous industries, including heavy machinery, tooling, and general manufacturing, utilize CNC machining for fabricating various components, molds, and prototypes.
Specific Examples of Products Manufactured Using CNC Machining
Precision Components: CNC machining is employed to manufacture precision CNC machining components such as gears, shafts, pistons, and valves with exacting tolerances and surface finishes.
Customized Parts: From specialized brackets and connectors to customized parts for specific machinery, CNC machining enables the production of tailored components.
Complex Prototypes: Companies use CNC machining to create intricate prototypes and models, facilitating the design validation process before mass production.
Intricate Designs: Intricately designed items like jewelry, artistic sculptures, and decorative elements benefit from the precision and accuracy of CNC machining.
Advancements and Future Trends in CNC Machining
Recent Technological Advancements in CNC Machining
Enhanced Automation: Recent years have seen a surge in automation within CNC machining. Integrated technologies enable higher levels of machine autonomy, reducing manual intervention and enhancing productivity.
Additive Manufacturing Integration: The integration of additive manufacturing (3D printing) with CNC machining has led to hybrid manufacturing systems. This fusion enables the creation of complex geometries and intricate designs with improved efficiency.
Advanced Tooling and Materials: Innovations in cutting tools and materials have expanded the capabilities of CNC machining. High-speed and high-precision tooling, coupled with the use of exotic materials, enhance performance and enable machining of previously challenging materials.
Machine Learning and AI Integration: Incorporating machine learning algorithms and artificial intelligence into CNC machining systems has improved predictive maintenance, optimized tool paths, and enhanced overall efficiency by learning from historical data.
Emerging Trends and Innovations in CNC Machining
IoT-Enabled Machining: The Internet of Things (IoT) integration in CNC machining systems allows real-time monitoring of machines, predictive maintenance, and remote control, optimizing operations.
5-Axis and Multi-Axis Machining: Advancements in multi-axis machining systems, especially 5-axis machines, provide enhanced capabilities for complex and intricate part production, reducing setups and increasing accuracy.
Digital Twin Technology: Utilizing digital twin technology in CNC machining creates virtual replicas of physical machines, allowing simulations for optimization, testing, and predictive analysis before actual production.
Environmentally Sustainable Machining: Developments in eco-friendly machining techniques, such as minimal lubrication or dry machining, focus on reducing waste, energy consumption, and environmental impact.
Predictions for the Future of CNC Machining Technology
Increased Integration of AI and Big Data: Expect more integration of AI-driven decision-making processes and the utilization of big data analytics to optimize CNC machining processes further.
Enhanced Hybrid Manufacturing Systems: Continued advancements in hybrid manufacturing systems combining CNC machining with additive manufacturing techniques will become more prevalent, enabling intricate and highly customized machining parts.
Augmented Reality (AR) in Machining: AR-assisted CNC manufacturing will likely emerge, offering real-time assistance, remote troubleshooting, and interactive training for operators.
Green and Sustainable Machining Practices: Continued emphasis on environmentally conscious machining practices will drive the development of sustainable techniques and materials, reducing the environmental impact of CNC machining manufacturing processes.
Future machining is poised for continued innovation and technological advancements, with a focus on automation, integration of emerging technologies, and sustainable manufacturing practices, promising greater efficiency, precision, and versatility in the industry.
Conclusion
Recap of Key Points about CNC Machining
Throughout this exploration, we've delved into the world of CNC machining, understanding its intricacies, and exploring its applications. Key takeaways include:
1.CNC machining is a computer-controlled manufacturing process that offers precision, efficiency, and versatility.
2.Various CNC processes such as milling, turning, and drilling cater to diverse industrial needs.
3.The importance of CAD/CAM CNC router software in design and production processes has revolutionized CNC machining.
4.CNC Machining’s applications span across industries, enabling the creation of complex and precise parts and components.
Final Thoughts About CNC Machining
CNC machining stands at the forefront of modern manufacturing, offering unmatched precision and efficiency in crafting intricate parts. Its potential knows no bounds, continually driving innovation and production capabilities.
Looking forward, CNC machining promises to revolutionize manufacturing, steering industries toward sustainability, higher precision, and increased automation, shaping the future of production.
To those curious or seeking optimized manufacturing, diving into CNC machining's intricacies holds immense value. Staying updated with advancements and embracing this technology empowers industries for innovation and competitiveness in today's dynamic landscape.
Exploring CNC machining opens doors to endless possibilities, fueling innovation within CNC precision manufacturing.
You Might also Like
View all →

CNC Milling Machine Operation: Ready to Master the Key Skills?
Read More →

How Much Does CNC Machining Cost?
Read More →





