How Much Experience Do You Have With
CNC Turning?
POSTED ON April 8
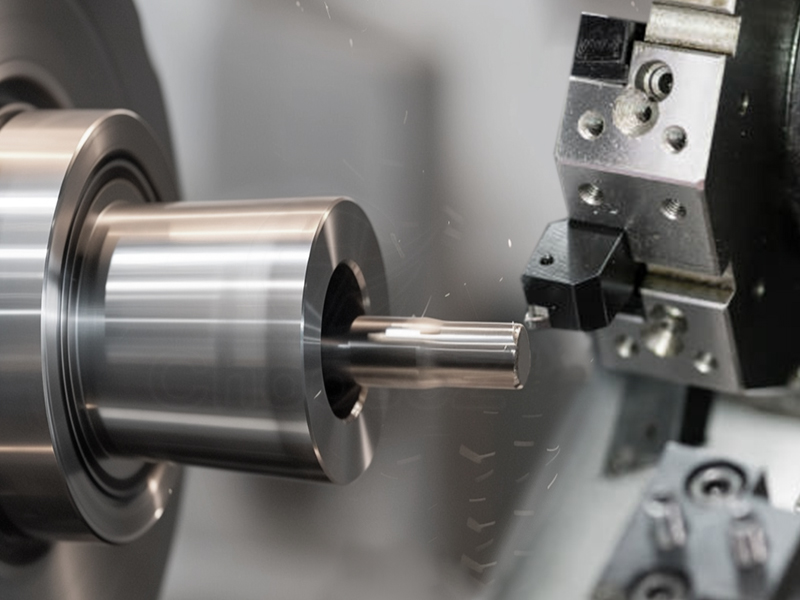

What Is CNC Turning?
CNC turning, also known as computer numerical control turning, is a type of machining in which a spinning workpiece is accurately machined to remove material using computerized controls. This subtractive manufacturing method is essential to modern production and is frequently used to produce cylindrical components.
To achieve the desired shape and dimensions, a raw material is secured in a CNC lathe and cutting tools are used to strategically remove extra material under the guidance of computer-programmed instructions.
What does CNC stand for?
The term CNC, or computer numerical control, refers to the computer-based automation of machine tools. Through the interpretation of numerical data, it provides accurate control over machining variables, such as cutting speed and toolpath. High precision and reproducibility in machining processes are guaranteed by this technique.
What is CNC turning and what is CNC Lathe?
You can simply remember that CNC turning and CNC Lathe are the same thing.
A workpiece is rotated during the CNC turning process in order to remove material and mold it into a cylindrical shape. A CNC lathe is usually used for this kind of work.
A CNC lathe is a type of machine tool that uses computer numerical control to automate and precisely regulate the turning operation. It allows for the fabrication of a variety of shapes by carefully arranging the cutting tool with respect to the spinning workpiece to create grooves, threads, and curves.
Because CNC turning on a lathe is so accurate and efficient, it is frequently used to produce cylindrical components.

What distinguishes CNC milling from CNC turning?
The methods used in CNC turning and CNC milling are two different machining processes with regard to how they remove material.
CNC turning is appropriate for circular or tubular items since it uses a stationary cutting tool in conjunction with a revolving workpiece.
On the other hand, CNC milling makes use of a revolving cutting tool and a fixed workpiece to produce a variety of holes, slots, and forms.
Turning is better at creating cylindrical parts, but milling is more flexible when it comes to forming intricate designs. The particular design specifications of the component being made will determine which option is best.
How do They Compare?
There are some important differences between CNC turning and CNC milling that should be noted.
Workpiece Rotation:
CNC turning: The cutting tool stays still as the workpiece rotates.
CNC milling: The workpiece stays still as the cutting tool spins.
Shapes Generated:
CNC turning is ideal for forms that are tubular or cylindrical.
CNC milling: Provides a flexible way to make different kinds of holes, slots, and forms.
Tool Motions:
CNC turning: The tool travels linearly along the diameter of the workpiece.
CNC milling: More complicated shapes are possible since the tool may move along many axes.
Uses:
CNC turning is perfect for cylindrical parts like bushings and shafts.
CNC milling is appropriate for a variety of products with complex geometry.
Fixture and Setup:
CNC Turning: Setup is usually easier.
CNC milling: Because the workpiece must be secured on several axes, this process may need a more complicated setup.

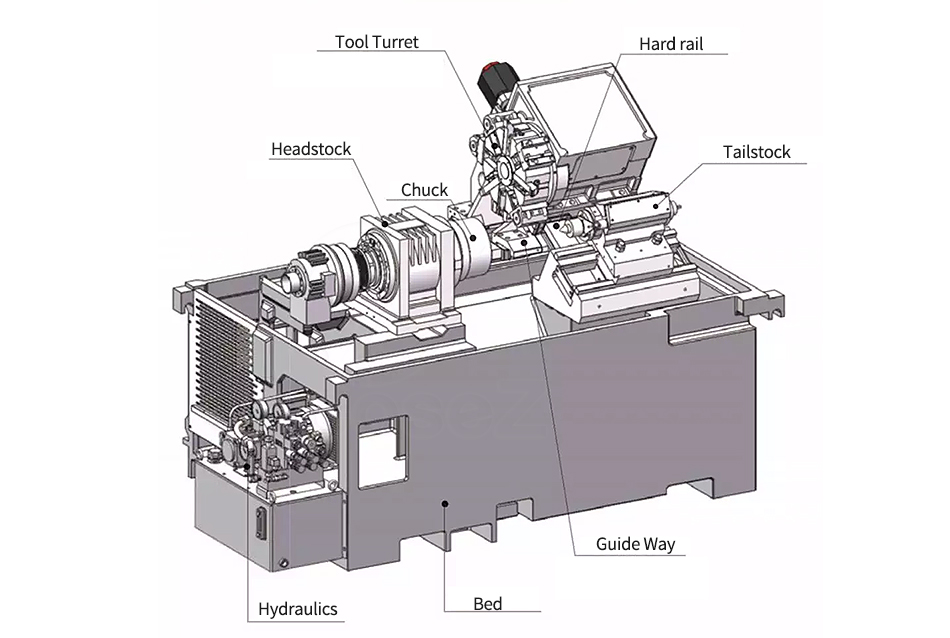
Components of A CNC Turning Machine
A CNC turning machine comprises several essential components that collectively contribute to its precision and functionality:
Bed: The foundational, horizontal structure supporting the machine components.
Headstock: Houses the main spindle and motor, responsible for rotating the workpiece.
Tailstock: Offers support to the other end of the workpiece, ensuring stability during machining.
Carriage: Moves along the length of the bed and contains the cutting tool.
Guideways: Provide a path for the movement of the carriage and tailstock, ensuring accuracy.
Chuck: Grips the workpiece securely and rotates it during the machining process.
Tool Turret: Holds multiple tools that can be automatically indexed for various machining operations.
Control Panel: Interface for programming and controlling the CNC machine, allowing operators to input commands.
CNC Controller: The brain of the machine, interpreting programmed instructions and translating them into precise movements and actions.
Understanding these components is crucial for efficient operation and programming of CNC turning machines.
Parameters of CNC Turning
In CNC turning, various parameters play a pivotal role in determining the outcome of the machining process. These parameters are essential considerations for achieving precision and efficiency:
Cutting Speed: The speed at which the cutting tool moves in relation to the workpiece. Influences material removal rate.
Feed Rate: The speed at which the cutting tool advances along the workpiece. Affects the quality of the machined surface.
Depth of Cut: The distance the cutting tool penetrates into the workpiece. Determines the material removal depth per pass.
Tool Offset:The programmed difference between the reference point and the actual cutting point on the tool. Adjusts for tool geometry.
Tool Nose Radius: The radius of the cutting tool's tip. Impacts the precision of the machined features.
Spindle Speed: The rotational speed of the spindle holding the workpiece. Influences cutting performance and tool life.
Coolant Flow: The rate at which coolant is delivered to the cutting zone. Manages tool temperature and chip evacuation.
Depth of Thread: The depth of the threads cut into the workpiece for threaded components.
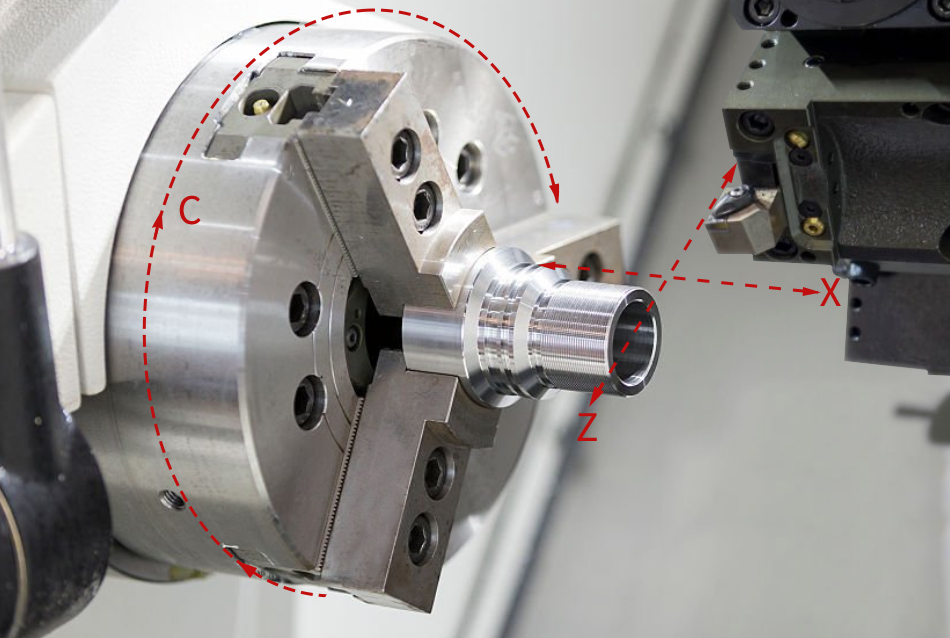
Axis Identification in CNC Turning/CNC Lathe
In CNC turning, the identification of machine axes is fundamental to understanding and programming the machining operations. The main axes in CNC turning, also applicable to CNC lathes, include:
X-Axis:
Represents the horizontal movement of the cutting tool along the workpiece's radial direction. It is typically aligned with the workpiece axis.
Z-Axis:
Represents the horizontal movement of the cutting tool along the workpiece's radial direction. It is typically aligned with the workpiece axis.
C-Axis:
Often found in advanced CNC lathes, the C-axis allows for the rotation of the workpiece. It adds versatility, enabling the machining of cylindrical features at different angles.
Comprehending these axes is essential for both toolpath control and programming. The C-axis offers extra rotational possibilities, and the X and Z axes regulate the tool's location. The secret to utilizing CNC turning machines to their maximum potential is mastery of axis identification.
Types of CNC Turning Machines
CNC turning machines come in various configurations to cater to different machining needs. The primary types include
2-Axis CNC Lathes: Fundamental and commonly used, these lathes operate with X and Z axes, making them suitable for simpler turning tasks.
Multitasking or Mill-Turn Machines: Combining turning and milling capabilities, these machines offer enhanced versatility by performing multiple operations in a single setup.
Swiss-Style Lathes: Ideal for precision machining of small, intricate parts, Swiss-style lathes use a sliding headstock and guide bushing for efficient and accurate production.
Vertical CNC Lathes: Featuring a vertical orientation, these lathes are suitable for large and heavy workpieces. They provide stability and ease of access.
CNC Screw Machines: Specialized for high-volume production of small parts, these machines excel in fast and efficient turning processes.
Types of CNC Turning Operations
A variety of operations are included in CNC turning to produce a workpiecewith a variety of shapes and features.Among the crucial turning operations are:
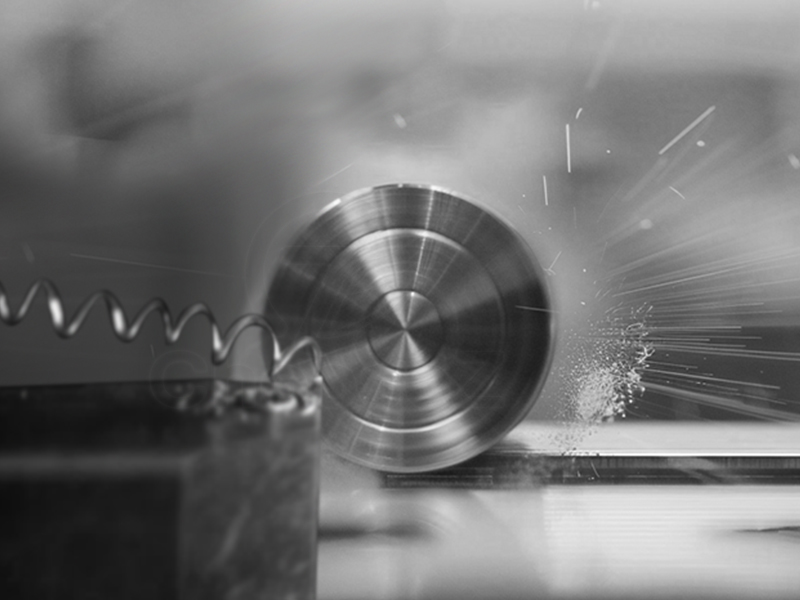

Facing:
Involves removing material from the end of a workpiece to create a flat surface.
Turning:
The main process that produces cylindrical shapes involves rotating the workpiece while moving the cutting tool parallel to the axis.
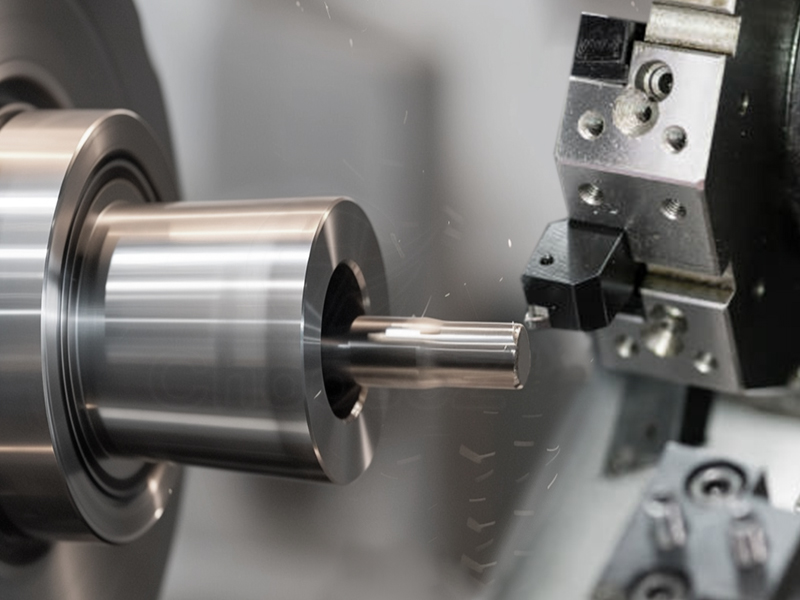
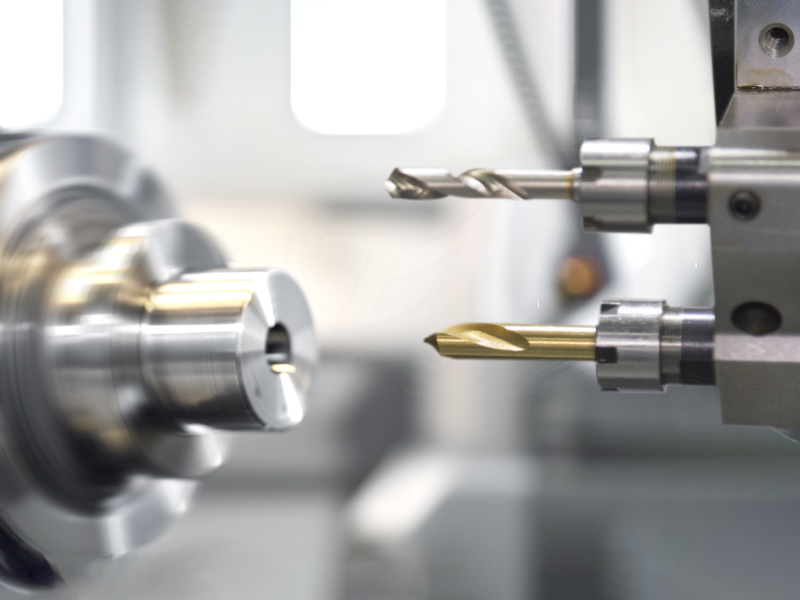


Drilling:
Drills holes in the workpiece by using a rotating tool. Precision drilling can be achieved with a variety of CNC turning machine operations.
Boring:
To ensure precise tolerances, existing holes are enlarged or their size are refined.
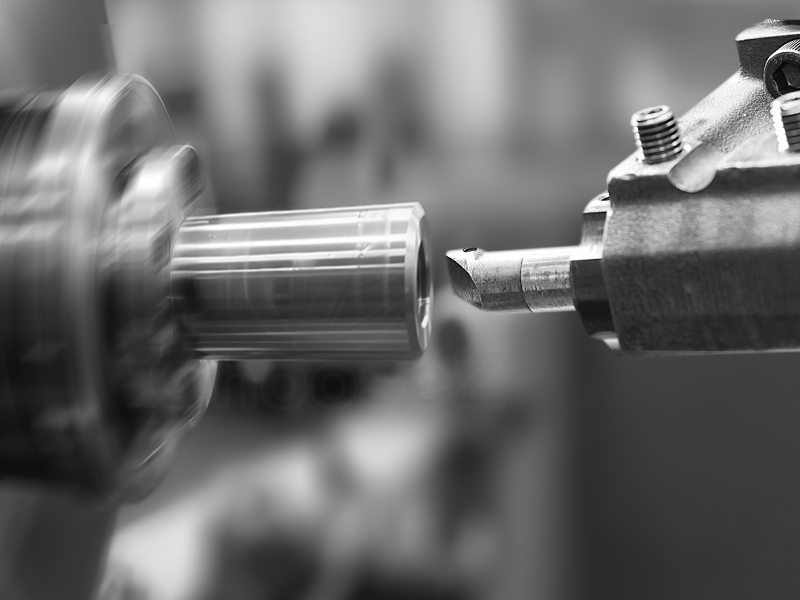
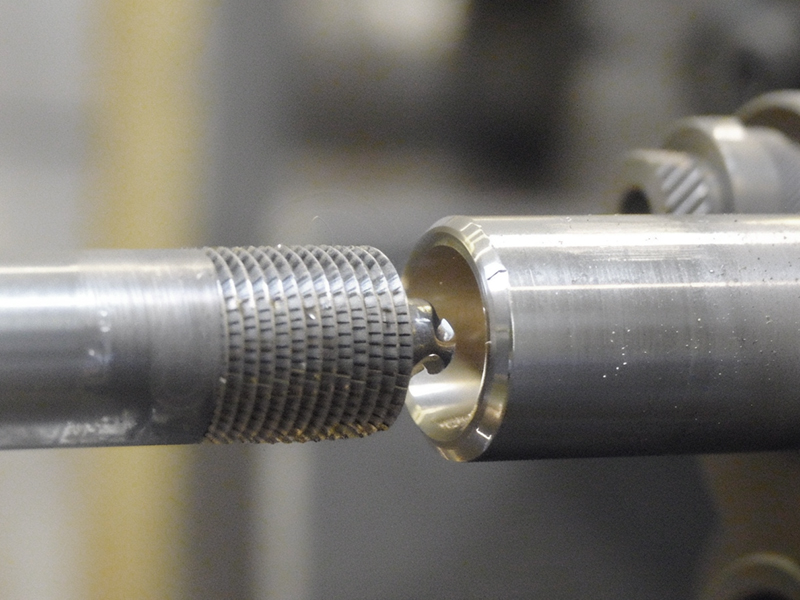
Knurling:
Textures the workpiece's surface to provide a better grip or for decorative purposes.
Threading:
Creates external or internal threads on the workpiece, allowing for the assembly of threaded components.
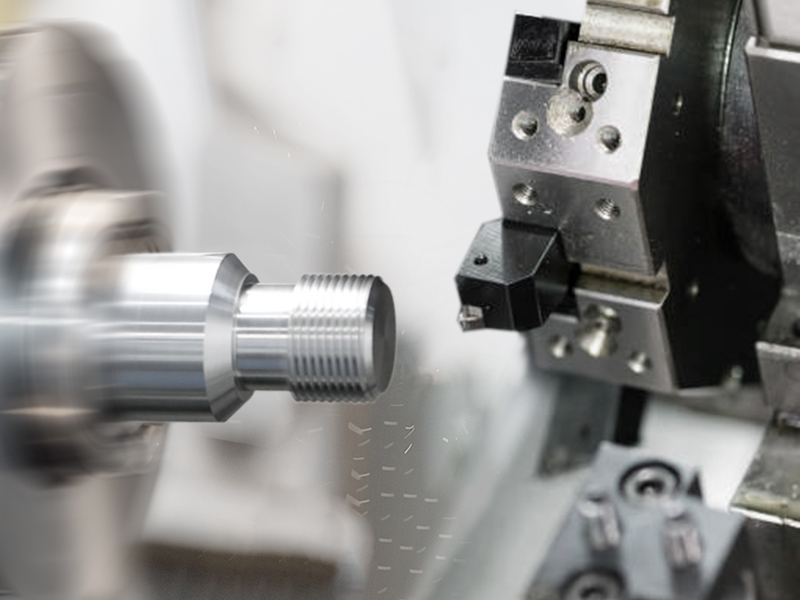
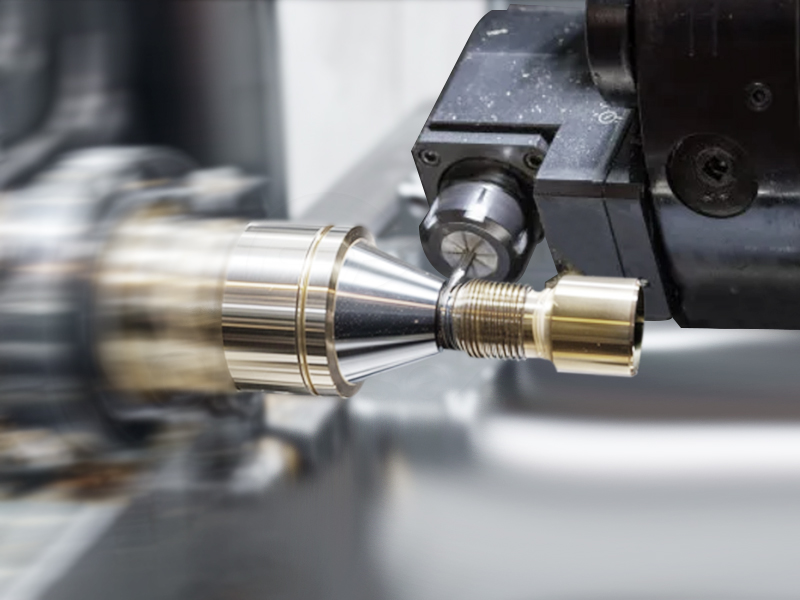


Grooving:
Involves cutting a narrow channel or groove on the surface of the workpiece, often for accommodating features like O-rings or retaining rings.
Parting Off:
Separates the finished part from the remaining material, completing the machining process.
Effective programming of CNC turning machines requires an understanding of these turning actions. It makes it possible to produce precise and complex parts consistently and efficiently.
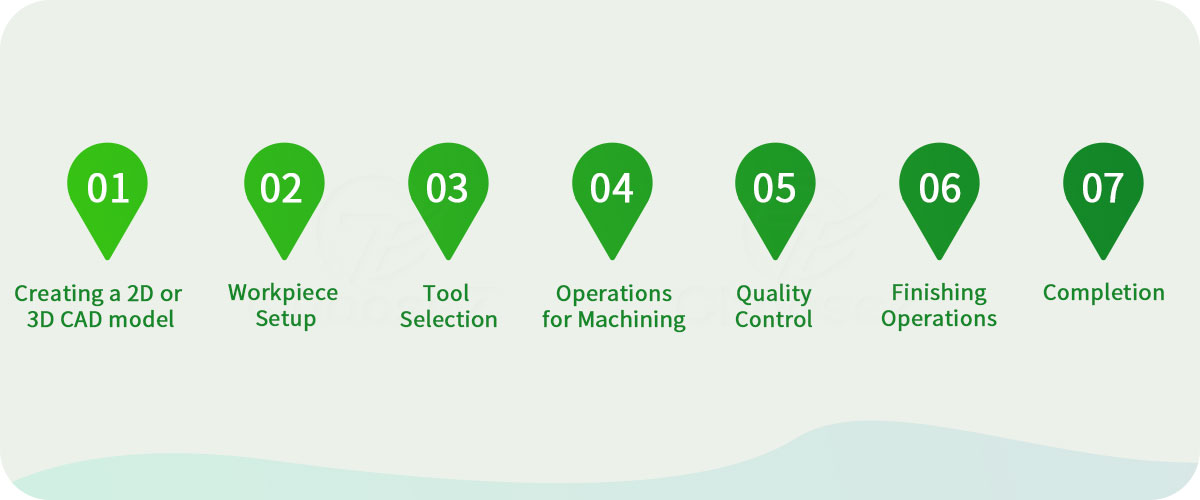
How CNC Turning Works
In general, the process of CNC turning is material is removed from a spinning workpiece using computer numerical control (CNC) equipment to generate cylindrical pieces,there are seven detailed steps:
1 Get ready: Creating a 2D or 3D CAD model of the part that needs to be made is the first step in the process.
A CNC programme is written by a programmer and comprises instructions that the CNC machine must follow while it is being machined.
2 Workpiece Setup: On a CNC lathe, a cylindrical workpiece—typically composed of plastic or metal—is firmly fixed.The workpiece is securely held in place while the machine spins by the chuck or collet.
3 Tool Selection: Depending on the workpiece's material and the required level of precision for the finished product, the right cutting tools—such as high-speed steel tools or carbide inserts—are chosen.
4 Operations for Machining: The operator of the CNC machine inserts the CNC program into the device and configures settings including feed rate, toolpath, and cutting speed. In order to remove material, the cutting tool travels along the length of the workpiece as the machine rotates it at a predetermined speed. Depending on the part design, CNC turning operations include drilling, contouring, threading, grooving, and facing.
5 Quality Control: To guarantee surface smoothness and dimensional correctness during machining, operators employ gauges, micrometers, and calipers, among other precision measuring instruments. To keep quality standards high and improve the machining process, modifications and continuous monitoring are possible.
6 Finishing Operations: If more machining, polishing, or deburring is required, it can be done after the main turning operations are finished.
7 Completion: The machined part is examined for correctness and quality when the machining process is complete.
Finished components are frequently tagged, cleaned, and ready for additional assembly or use in the finished product.
Is the Workpiece The Only Part Which Moves?
No, in CNC milling, the workpiece and the milling machine are both mobile. In CNC turning, the spindle and bed of the milling machine move dynamically in many axes, but the workpiece stays immobile. This increases the machining processes' adaptability by enabling the cutting tool to approach the workpiece from various angles.
What Forms Is CNC Turning Capable of ?
CNC turning is flexible and can create a range of shapes, such as:
Cylindrical Shapes:
Turning is a very good way to make cylindrical objects like tubes and shafts.
Conical Shapes:
This method increases the variety of machined components by achieving conical features.
Spherical Shapes:
Spherical shapes can be produced by CNC turning, which helps to produce rounder components.
complicated Contours:
A greater variety of shapes can be created by achieving detailed and complicated contours with the use of sophisticated tooling and programming.
CNC turning is a favored method for producing parts with a variety of geometric characteristics because of its flexibility.
Common Raw Materials Can be Used In CNC Turning

A variety of raw materials can be used with CNC turning, including:
Metals: Stainless steel, brass, aluminum, and other common metals are commonly used in CNC turning because of their machinability and longevity.
Plastics: A variety of engineering plastics, including ABS, PEEK, and nylon, are suitable for CNC turning and provide adaptability for a range of uses.
Wood: CNC turning is often used on wood to create intricately designed and personalized wooden components.
Exotic Materials: Specialized businesses might be satisfied by CNC turning's ability to handle exotic materials like Inconel and titanium.
History of CNC Turning
The origins of CNC turning can be found in the mid-1900s with the introduction of numerical control (NC) systems. The following significant junctures are listed:
1950s: The first step was made possible by the introduction of NC machines, which punched cards with numerical codes to automate manual machine operations.
1960s: CNC machines developed the ability to understand digital data with the advent of computer technology, allowing for more intricate and accurate control.
1970s: As computer technology developed further, CNC turning in particular became more popular because it offered increased manufacturing flexibility for parts.
1980s–1990s: As a result of ongoing improvements in hardware and software, CNC turning became extensively used in a variety of sectors.
21st century: For smooth design-to-production processes that guarantee accuracy and efficiency, contemporary CNC turning machines incorporate cutting-edge technology like CAD/CAM.
The history of CNC turning reflects a continual march of technological progress, transforming manufacturing into a highly automated and precise endeavor.
Advantages of CNC Turning
CNC turning is a recommended option in production operations since it provides a number of benefits. The following are the main advantages:
Accuracy & Precision: Unmatched precision is provided by CNC turning, guaranteeing precise and consistent outcomes throughout every manufacturing cycle. For industries where strict tolerances are necessary, this is essential.
Automation and Efficiency: CNC turning's automated nature minimizes the need for manual intervention, which boosts productivity and speeds up production. This reduces the possibility of mistakes that come with manual milling as well.
Flexibility in Materials: CNC turning is capable of working with a broad variety of materials, including plastics and metals, which makes it possible to manufacture a variety of components. This adaptability is crucial for a range of industry demands.
Complex Geometries: The capability to produce intricate shapes and complex geometries sets CNC turning apart. It enables the manufacturing of parts with detailed features that may be challenging or impossible with traditional methods.
Cost-Effectiveness: While initial setup costs may be higher, CNC turning becomes cost-effective for large production runs due to its efficiency and reduced material wastage. It offers long-term economic benefits.
Consistency in Production: CNC turning ensures consistency across batches, reducing variations in the final products. This is crucial for maintaining quality standards and meeting stringent specifications.
Alternatives of CNC Turning
Although there are many benefits to CNC turning, other alternative machining techniques meet different manufacturing needs. Notable substitutes for CNC turning include as follows:
CNC Milling: Using rotary cutting tools to remove material from a workpiece, milling is different from turning. It can be used to create features, complex details, and three-dimensional shapes on a variety of surfaces.Common CNC milling methods include 5-axis CNC milling.
Wire EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining): This process uses electrical discharges to shape the workpiece. It is particularly effective for intricate and delicate parts, offering high precision.
Waterjet Cutting: This method of cutting through materials involves using a high-pressure stream of water that has been combined with abrasive particles. For softer materials and circumstances where heat generation is an issue, it is perfect.
Laser Cutting: This method of cutting materials uses a concent rated laser beam. It works well with thin materials and offers excellent precision, particularly in fields like electronics.
Plasma Cutting: Ionized gas is used in plasma cutting, which is a common method of cutting metal, to melt and remove material. It works well for high-speed cutting and thick materials.
3D Printing/Additive Manufacturing: This cutting-edge method creates a final object by layering up material. It is excellent at producing complex geometries and prototyping quickly.
The best machining technique to use will depend on a number of variables, including the material, part complexity, and production volume. Every option has advantages of its own, enabling manufacturers to choose the best procedure for their particular requirements.
Applications of CNC Turning
CNC turning, with its precision and versatility, finds application across various industries for the production of intricate components. Here are key applications of CNC turning:
Automotive Components: Shafts, bushings, and pulleys are among the many vehicle parts that are produced using CNC turning. Its capacity to manufacture precision parts enhances the dependability and efficiency of automotive systems.
Aerospace Parts: CNC turning is used to make turbine shafts, engine mounts, and hydraulic fittings in the aerospace sector, where accuracy is essential. Tight tolerances and flawless surface finishes are required for these parts.
Medical Devices: The creation of surgical implants, bone screws, and instrument parts relies heavily on CNC turning. The procedure guarantees the creation of hygienic, highly accurate medical equipment.
Electronics: CNC turning is useful in the electronics industry for producing parts like as terminals, connections, and specialty pieces for electronic equipment. The procedure ensures precision in complex electronic parts.
Hydraulic and Pneumatic Components: CNC turning is frequently used in the manufacturing of cylinders, valves, and fittings, among other hydraulic and pneumatic system parts. For these components to work as best they can, accuracy is needed.
Tooling and Fixtures: To make the tooling and fixtures required for different machining operations, manufacturers use CNC turning. These instruments are essential for guaranteeing precision and effectiveness in manufacturing.
Customized Parts: CNC turning makes it possible to produce unique, specialized parts that are suited to certain industrial requirements. Because of its adaptability, it can be used for a variety of bespoke manufacturing needs.
How Can You Determine Whether CNC Turning Is The Best Option For Your Part?
For products that need cylindrical characteristics, including shafts, pins, and bushings, CNC turning is the best option. To decide if CNC turning is right for your part, take into account the following important factors:
Cylindrical Geometry: If your part has rotational symmetry or needs features like holes, threads, or grooves along its axis, CNC turning is highly effective. It excels at creating cylindrical shapes with precision.
Efficient for Medium to High Volumes: CNC turning is well-suited for producing parts in medium to high volumes. Once the lathe is set up, it can consistently and rapidly produce identical cylindrical components.
Tight Tolerances: CNC turning is a dependable option if your design calls for extremely precise and tight tolerances. Accurate control over surface finishes and dimensions is made possible by the procedure.
Materials Compatibility: Metals, polymers, and composites are just a few of the materials that CNC turning is effective with. It is adaptable enough to meet numerous projects' material requirements.
Take the manufacturing of a specially designed metal shaft for a piece of machinery, for instance. The shaft is ideal for CNC turning due to its cylindrical shape and features, such as threads at both ends. Because of the process's efficiency, identical shafts may be made in huge quantities, meeting manufacturing needs quickly and precisely.

ChooseZ CNC Turning Service
ChooseZ is a dependable partner when it comes to CNC turning precise manufacturing. The following best describes our CNC turning service:
Modern Technology: Modern CNC turning machines with cutting-edge features are used by ChooseZ. This guarantees the highest caliber of accuracy and productivity when producing your components.
Expertise in Machining: Our group of knowledgeable machinists is well-versed in managing CNC turning procedures. Their experience ensures that every job is completed with the highest caliber and meticulousness.
Tailored Solutions for Diverse businesses: ChooseZ offers CNC turning solutions that are specifically designed to meet the demands of different businesses. Whether it's the automotive, aerospace, or medical industries, we customize our services to fit the unique needs of each.
On-Time Delivery: At ChooseZ, effectiveness is our top priority. Your projects are given the highest attention, and we guarantee prompt delivery without sacrificing the caliber of the finished result.
Discover the accuracy and dependability of ChooseZ's CNC turning capabilities. Upgrade your manufacturing skills by selecting ChooseZ as a reliable partner.

Micheal Wu
Engineer Manager
Wu is a mechanical engineer with more than ten years of experience.His personality is not boring but very interesting. He is also very good at cooking, so he always plays the role of chef during team building.
You Might also Like
View all →

CNC Milling Machine Operation: Ready to Master the Key Skills?
Read More →

How Much Does CNC Machining Cost?
Read More →









